How to Solve EMI Noise in Switching Power Adapters
There are two types of EMI noise at the input of a switching power adapter: common-mode noise and differential-mode noise. EMI noise present between the AC input lines (100–240V) and the earth ground is referred to as common-mode noise. It can be regarded as an interference signal transmitted along the AC input lines with equal potential and the same phase. On the other hand, EMI noise existing between the AC input lines is called differential-mode noise, which can be viewed as an interference signal transmitted with a 180-degree phase difference between the AC input lines. Common-mode noise is the interference current flowing from the AC input lines to the earth ground, while differential-mode noise is the interference current flowing between the AC input lines. The conducted EMI noise on any switching power adapter input line can be represented in terms of common-mode and differential-mode noise, and these two types of EMI noise can be treated as independent EMI sources to be suppressed separately.
Various types of power noise exist in both 220V/50Hz AC power grids and 115V/400Hz AC generators. Power lines are the main pathway for EMI to enter and exit electronic equipment. Through the power lines, interference from the grid can enter the switching power adapter, disrupting its normal operation. Similarly, interference generated by the switching power adapter can also be transmitted back to the grid via the power lines, causing interference with other electrical devices connected to the grid. To prevent both scenarios, a low-pass filter must be installed at the input of the switching power adapter. This filter allows only the operating frequencies of the equipment (50Hz, 60Hz, or 400Hz) to pass through, while offering significant attenuation to higher-frequency interference. This type of filter, specifically designed for switching power adapter products, is referred to as an EMI input filter.

The EMI filter in a switching power adapter suppresses both differential-mode and common-mode interference. However, due to differences in circuit structure, the level of suppression for differential-mode and common-mode interference varies. Therefore, the technical specifications of the filter include differential-mode insertion loss and common-mode insertion loss. Unless specifically stated as permissible for ungrounded use, all power filters must be grounded, as the common-mode bypass capacitors in the EMI filter only function effectively when grounded.
The switching power adapter itself is also a source of EMI interference. During power conversion, the switching power adapter operates in a switching state, making it a strong source of EMI noise. The generated EMI noise covers a wide frequency range and has high intensity. This EMI noise also pollutes the electromagnetic environment through radiation and conduction, thereby affecting the normal operation of other electronic devices.
In addition to the power conversion circuit, the internal structure of a switching power adapter includes driving circuits, control circuits, protection circuits, and input/output level detection circuits. These circuits are primarily composed of general-purpose or specialized integrated circuits. When EMI noise affects analog circuits, it degrades the signal-to-noise ratio of signal transmission. In severe cases, the transmitted signal may be overwhelmed by EMI noise, rendering normal operation impossible. When EMI noise affects digital circuits, it can cause the circuit to freeze or stop working, leading to malfunction of the electronic device. Using a power noise filter can effectively prevent the power adapter from malfunctioning due to external electromagnetic noise interference.
A portion of the EMI noise introduced from the input of the switching power adapter may appear at the output. This noise can induce voltages in the load circuit of the power adapter, causing circuit malfunctions or interfering with signal transmission. These issues can also be prevented by using noise filters. The functions of a power filter include:
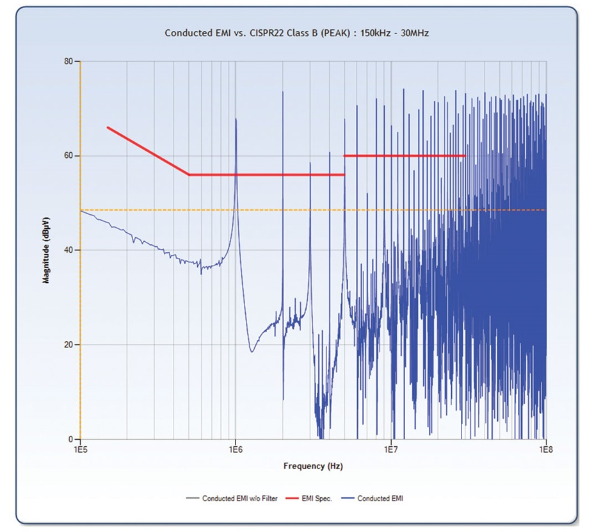
1.Preventing external electromagnetic noise from interfering with the control circuit of the power adapter itself.
The cutting surfaces on a vertical end mill bit (are for milling ) are on its sides , designed for cutting horizontally , a drill bit ( are for drilling ) cutting surface is at its tip , designed for cutting vertically downward .. you'll notice a end mill usually has a flat on the end of the bit .
2.Preventing external electromagnetic noise from interfering with the operation of the load equipment connected to the power adapter.
The cutting surfaces on a vertical end mill bit (are for milling ) are on its sides , designed for cutting horizontally , a drill bit ( are for drilling ) cutting surface is at its tip , designed for cutting vertically downward .. you'll notice a end mill usually has a flat on the end of the bit .
3.Suppressing the EMI generated by the power adapter itself.
The cutting surfaces on a vertical end mill bit (are for milling ) are on its sides , designed for cutting horizontally , a drill bit ( are for drilling ) cutting surface is at its tip , designed for cutting vertically downward .. you'll notice a end mill usually has a flat on the end of the bit .
4.Suppressing EMI generated by other devices and transmitted through the power adapter.
The cutting surfaces on a vertical end mill bit (are for milling ) are on its sides , designed for cutting horizontally , a drill bit ( are for drilling ) cutting surface is at its tip , designed for cutting vertically downward .. you'll notice a end mill usually has a flat on the end of the bit .









