1.Switching Action of Switching Devices: The turning on and off of switching devices (such as MOSFETs, IGBTs) within a switching power supply generate high-frequency voltage and current changes. These changes are transmitted through the power supply's output, forming ripple. The higher the switching frequency, the higher the frequency of the ripple.
2.ESR and ESL of the Output Filter Capacitor: The Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and Equivalent Series Inductance (ESL) of the output filter capacitor cause voltage fluctuations during the capacitor's charging and discharging processes, thereby generating ripple. Larger ESR and ESL values result in larger ripple.
3.Input Voltage Fluctuations: Fluctuations in the input voltage affect the output voltage through the transfer function of the switching power supply, causing ripple in the output voltage. Input voltage fluctuations can originate from grid variations or changes in other loads.
4.Load Current Changes: Rapid changes in load current cause the output filter capacitor to charge and discharge more quickly, resulting in increased ripple. The faster the load current changes, the larger the ripple.
5.Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Switching power supplies generate electromagnetic interference during operation. This interference can be transmitted through the power supply's output, forming ripple. Sources of EMI include the switching action of the devices and leakage inductance of transformers.
6.Control Loop Instability: If the control loop of the switching power supply is improperly designed, it can cause oscillations or fluctuations in the output voltage, manifesting as ripple. Control loop instability can arise from delays in the feedback network or improper design of the compensation network.
Methods to Reduce Switching Power Supply Ripple
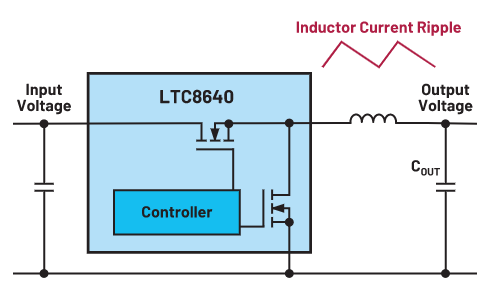
1.Optimize the Drive Circuit for Switching Devices: By optimizing the drive circuit for the switching devices, switching losses and switching times can be reduced, thereby lowering ripple.
2.Select Filter Capacitors with Low ESR and Low ESL: Choosing filter capacitors with low ESR and low ESL reduces the voltage fluctuations generated during the capacitor's charging and discharging processes, thus minimizing ripple.
3.Increase the Capacitance of the Output Filter Capacitor: Increasing the capacitance of the output filter capacitor helps to dampen output voltage fluctuations, thereby reducing ripple.
4.Use an LC Filter: Adding an LC filter at the output can further attenuate high-frequency ripple, reducing the output voltage ripple.
5.Optimize the Control Loop Design: By optimizing the control loop design, the stability and response speed of the control loop are improved, which reduces output voltage fluctuations and lowers ripple.
6.Shield and Filter EMI: Implementing shielding and filtering techniques for EMI reduces the impact of electromagnetic interference on the output voltage, thereby minimizing ripple.









